Today’s commercial and industrial settings involve heavy machinery and complex electrical and electronic systems. The drive for productivity and automation has introduced the preponderance of electronic components driving systems and processes everywhere.
This race for optimum performance, efficiency, reliability, safety and business competitiveness has placed power quality in the front burner as a result of the electronic evolutional they are susceptible to the quality of power or power quality.
A good power quality in a facility guarantees overall business competitiveness.What then is Power Quality?

Power Quality Defined
Power quality means different things to different people based on their perception. However the following definitions offer a guide to understanding the subject matter.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) describes power quality as “the concept of powering and grounding sensitive equipment in a manner that is suitable to the operation and compatible to the premise wiring system and their connected equipment.”
In other words power quality problems can be defined as any power problem manifesting in voltage, current or frequency deviations that result in failure or mis-operation of utility or end user equipment “Electrical Power Systems Quality” by Roger Dugan, Mark McGranaghan, and Wayne Beaty.
In the work setting PQ has become an everyday and everybody concern.
How?
Power Quality concerns and their symptoms?
It is common in facilities to experience computer lock ups, malfunction, mis-operation or damage.
Nuisance tripping of circuit breakers, relay and contractors.
Sensitive equipment malfunctioning or crashing intermittently like Programmable logic controllers(PLC’s), adjustable speed drives(ASD’s) variable frequency drives(VFD’s), loss of data, loss of synchronization of process equipment, noise interference with signals and telephones lines.
Motor, cables and transformers overheating, malfunction or damaged, light flickers or dim and electric shocks.
The LCM of these issues is simply Poor Power Quality (PQ).
Clear Implications

If your PQ is poor or what is not supposed to be your facility is losing MONEY through:
- Downtime
- Equipment problems/ maintenance
- Energy loss
The ultimate result being downtime (unreliable electrical systems), decreased productivity, frustrated personnel and reduced business competitiveness.
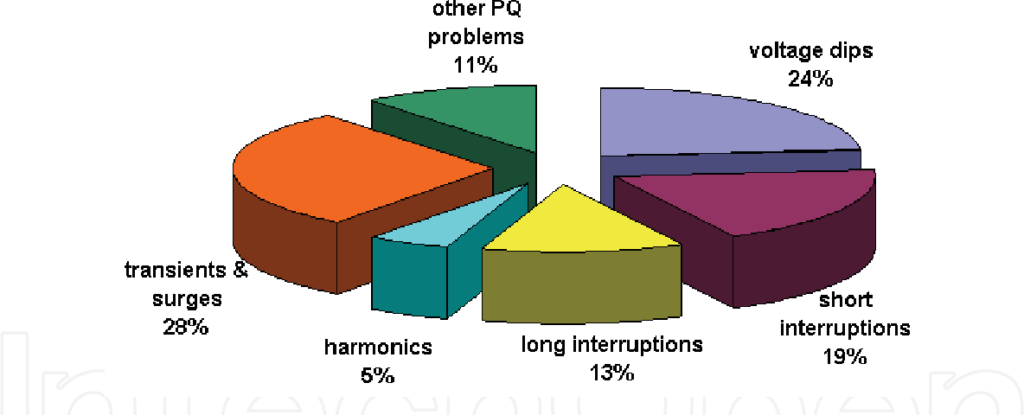
Today, we shall start in a nutshell discussing 12 common power quality problems that are usually encountered in the workplace.
If understood , and appropriate mitigation which involve, a combination of strategies, including but not limited to, installing power conditioning equipment, using power management systems to monitor and control power quality, implementing regular maintenance schedules, and working closely with utility providers to ensure a stable power supply.
That ensures business transition from the red to the black in the balance sheet. They are:
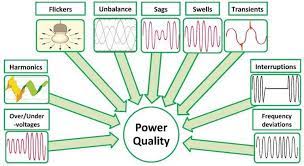
1. Voltage Sags (Dips)
Short-term decreases in voltage levels often caused by the startup of large equipment, utility grid switching, or faults in the power system.
2. Voltage Swells
Short-term increases in voltage levels, which can occur due to sudden load reductions or problems with voltage regulation on the power grid.
3. Transients (Spikes and Surges)
Very brief, high-voltage spikes that can be caused by lightning strikes, power outages, or switching of electrical loads.
They can damage sensitive electronic components.
4. Harmonic Distortion
Distortion of the normal AC waveform, typically caused by non-linear loads such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), switching power supplies, and heavy electronic equipment.
Harmonics can lead to overheating of equipment, reduced efficiency, and interference with communication systems.
5. Flicker
Are visible fluctuations in lighting intensity, which can be caused by intermittent loads or starting and stopping of heavy machinery.
Flicker can be distracting or uncomfortable for workers and can affect sensitive processes.
6. Frequency Variation
Deviation from the standard frequency (e.g., 50Hz).
This occurs mostly in isolated power systems or with generator use.
Frequency variations affect the operation of sensitive equipment and timing devices.
7. Voltage Imbalance
Usually occur in three-phase systems, when the voltage or current in one or more phases differ from the others.
Resulting in motor overheating, reduced performance, and increased energy consumption.
8. Electrical Noise
Electromagnetic interference from various sources, including motors, switches, and radio transmitters, can cause communication errors and affect sensitive equipment.
9. Brownouts
Prolonged period of low voltage, which could be intentional (used to reduce demand on the grid) or due to problems with the power supply.
Brownouts can cause equipment to operate inefficiently or shut down.
10. Blackouts
Complete loss of power supply, usually caused by utility failure, grid issues, or natural disasters.
Blackouts halt all production and can lead to data loss and safety concerns.
11. Voltage Fluctuation
In general terms, any variation in voltage that can cause lights to dim or brighten and can affect sensitive equipment.
12. Phase Loss
Also known as “single-phasing”, occur when one phase of a three-phase system is lost.
It can result from a blown fuse, a broken wire, or a utility fault and can cause serious damage to three-phase motors and equipment.

At FullSpectrum Energy, we understand various voltage disturbances and issues. We know that these issues operate in gang.
With FullSpectrum power quality lens, we are uniquely equipped to eliminate, mitigate and offer tailored cost effective solutions to these plethora challenges.
If you are struggling with power issues and it is definitely affecting your competitiveness irrespective of your industry.

FullSpectrum Solutions, your reliable partner is just a chat or a call away.
Book for a free survey


Power Quality and Energy Management Specialist.
Publisher at Afrienergyonline.com
CEO, FullSpectrum Energy Solutions Limited, Nigeria.